This paper conducts a research on modulation characteristics of blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) used in a visible-light communication (VLC) system. Through analysis of the modulation characteristics of LEDs with different emitting sizes, we find that there is a similar linear relationship between LED’s 3dB bandwidth and the operation current density. This experiment also shows that high series resistance is one major issue that limits our LED's modulation speed. To further improve the LED bandwidth, the resistance can be reduced by optimizing device layout as well as reducing material bulk resistance. Clearly, this study provides an approach to increase the modulation bandwidth of GaN-based LEDs for VLC systems.
With the rapid development of modern solid-state lighting, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are increasingly used in a wide range of display, signaling and illumination applications. Because of the long lifetime and high energy efficiency, LED is becoming one of the dominant illumination technologies. In addition, these small-sized and energy-efficient devices tend to be used in both illumination and communication: visible-light communication (VLC) is attracting a lot of research interests in Asia, Europe and the U.S. Using GaNbased LEDs as the signal sources in VLC systems, the modulated signal is able to transmit digital data beyond the perception speed of human eyes. Therefore, the double functions of LEDs make them popular in recent researches on the area of free space VLC system.
A typical LED’s current-voltage (I-V) curve is clearly known. The LED is single conduction and when the bias voltage exceeds a certain turn-on value VA, the LED can operate in the linear region (work area). The turn-on voltage of the LED in this study is about 2.8 V. Therefore, in order to ensure the LED work in the linear region, the bias voltage should be higher than 3 V. The modulation capability of a LED is described with optical power and electrical current (P-I curve). In Figure1, the P-I curve was approximately linear without a threshold current, so the LED’s optical power output can be linearly modulated with a small input voltage signal that is biased above VA.
The bandwidth measurement setup for the VLC system is shown in Figure 2 and the parameters of each component were listed in Table 1. The VLC transmitter consists of an amplifier a power supply and a bias-T. The receiver comprises a photo-detector that was PositiveIntrinsic Negative diode (PIN diode) or Avalanche Photo Diode (APD). LED that was the light source in transmitter emits visible light and then absorbed by receiver through free space spread. The two-port network analyzer works as a signal source and also a terminal analyzer, providing a small sine wave as a function generator and measuring the received amplitude as well.
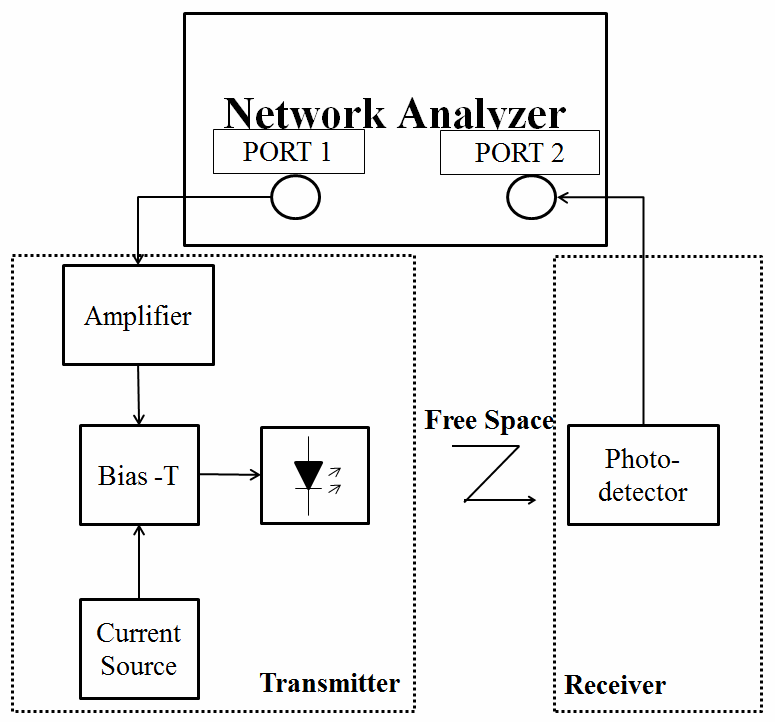
Fig1
The three different experimental LEDs were divided into three groups, which were measured under the same light intensity, and then current density became the only variable. Therefore, the results can directly reflect the relationship between current density and the 3 dB bandwidth of LED. In Figure 3, the Y coordinates, which is S21 Amplitude, means that the ratio between output power and input power and it reflects the 3 dB bandwidth of LED. Because of the background noise in this experiment, the curves in Figure 3 have large fluctuations. However, these non-smooth curves are not affecting the overall trend of the experimental results.
In this paper, a measurement setup of modulation characteristics for VLC systems is described and the bandwidths of different-sized blue LEDs have been reported. The results clearly reveal a similar linear relationship between LED current density and its 3dB bandwidth. This phenomenon can be attributed to the bimolecular recombination probability that is proportional to the injected carrier density into the active volume. Therefore, increasing the LED current density is a feasible method in VLC systems to enhance the data transmission rate. Moreover, this experiment shows that high series resistance is one major issue that limits our LED's modulation speed. Thus, further study will focus on optimizing device layout as well as reducing material bulk resistance to reduce the resistance.