Copper Oxide (CuO) thin films, a candidate for PSC and p-n junction SCs, were deposited on glass substrates bychemical bath deposition (CBD) and effects of annealing at 300, 350, 400, 450, and 500 ◦C for 1 h in a mufflefurnace on different physical properties were studied. XRD spectra matched well with monoclinic nature of CuO.XRD results revealed that with increasing annealing temperature, crystallite size increased. Raman spectroscopycon firmed development of CuO phase. UV–vis spectroscopy showed excellent photo absorption in the visibleregion of incident sun light and absorption coefficient remained high. Optical bandgap energy decreased in therange of 1.45 to 1.52 eV with increasing annealing temperatures. Conductivity type observed by thermoelectric/hot probe confirmed the p-type conductivity. The obtained results suggest that CuO thin films with excellentoptical properties and p-type nature could be reliably companioned with n-type layer in both n-i-p PSC and p-njunction solar cell structures.
To prepare CuO thin films, a high purity copper acetate (Cu(CH3COO)2, 99.999 % purity) source material was purchased fromSigma Aldrich and used as purchased. Aqueous ammonia solution wasused to keep pH value about 11 and diethanolamine (DEA) was used as acatalyst to control reaction. DEA is a colorless reagent found as powderor viscous liquid that is used as a solvent and stabilizer. Microscopicglass slides were used as substrate material.
Before the deposition of CuO thin films, glass substrates were cleanedvigorously. At first step the glass substrates were cleaned with detergentfor 15 min, and after this, substrates were rubbed in distilled water byusing electric tooth brush and detergent. Next, the glass substrates werewashed ultrasonically in IPA and then in acetone for 10 min eachrespectively and later dried at 60 ◦C in an oven. All these well cleanedsubstrates were kept in IPA before deposition.
Copper acetate (Cu(CH3COO)2, 99.999 % purity) was used as starting material for the synthesis of copper oxide thin films and CuO thinfilms were deposited by chemical bath deposition technique on the wellcleaned glass substrates (Reyes-Vallejo et al., 2022). Copper acetate wasdissolved in 100 ml distilled water to prepare a 0.1 M concentrationsolution. The solution was stirred at room temperature for 1 h in order toget a well dissolved homogeneous solution. The pH value of the solutionwas maintained at 11 by adding aqueous ammonia. When temperatureof this solution reached at 90 ◦C, cleaned glass substrates were dippedfor 15 min in the solution and copper was deposited on these substrates(Mude et al., 2022). This same process was repeated to prepare somemore samples. The deposited thin films were then dried at 60 ◦C for 10min in an oven. Dried samples were rinsed in distilled water to removelarger and loosely bounded particles on the surface. These prepared thinfilms were then annealed in a box furnace at different temperatures(300, 350, 400, 450 and 500 ◦C) for 1 h.
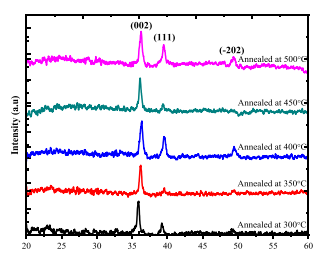
Fig1
Thickness plays an important role in rendering physical properties tothe thin films. Thickness of prepared thin films were calculated usingmass difference method (Wang, 2021). The mass of the thin films wascalculated by measuring mass of prepared samples two times, firstbefore thin film deposition (bare glass slides) and then after the deposition of thin films on glass slides. Then the difference of the masses“Δm” provided the mass of thin film deposited on the substrate. Densityof CuO and volume of the glass substrate are 2.5 g/cm3 and 75 × 25 × 1mm3 respectively. Finally, the thin film thickness was calculated according to the following equation (1), (Akl and Hassanien, 2021).
上一篇: 提高蚀刻速率均匀性和减少聚合物堆积的方法
下一篇: 使用 TMAH 溶液垂直蚀刻氮化铝铝薄膜