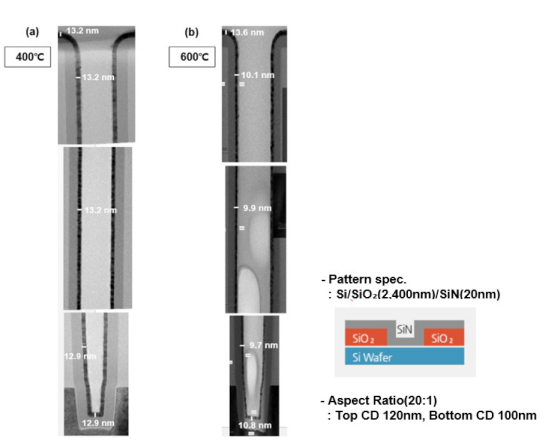
热原子层沉积 TiN 薄膜沉积温度的影响
In this study, the effect of deposition temperature of TiN thin films deposited using the thermal atomic layer deposition (ALD) method was investigated. TiCl4 precursor and NH3 reactive gas were used, and the deposition rate, resistivity change, and surface morphology characteristics were compared in the deposition temperature range of 400 ◦C–600 ◦C. While resistivity decreased to 177 µΩcm as the deposition temperature increased to 600 ◦C, an increase in surface roughness (Rq) to 0.69 nm and a deterioration in the step coverage were identified. In order to obtain a high-quality TiN thin film with excellent resistivity and step coverage characteristics even at low deposition temperatures, the TiN thin film was post-treated with plasma in a combination of N2/He gas ratio of 3:2 to confirm the change in resistivity.
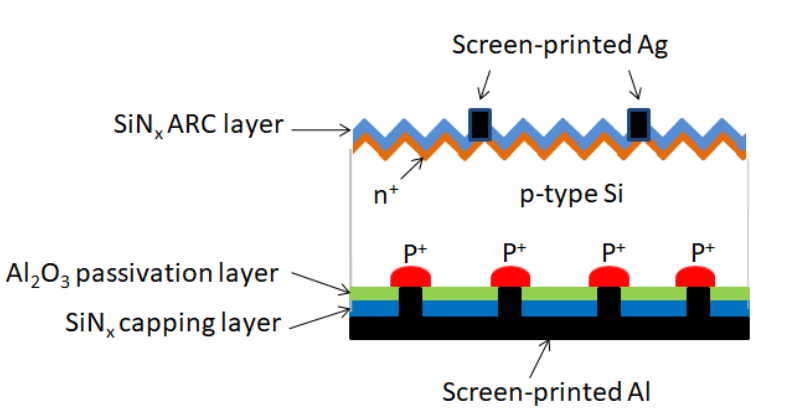
用于 p 型晶体硅表面表面钝化的溶液处理氧化铝薄膜
Efficient and inexpensive photovoltaic systems are necessary to meet the increasing global electricity demand. In order to improve the efficiency of the crystalline silicon (c-Si) solar cells, the recombination losses of charge carriers must be reduced by the surface passivation techniques. Aluminium oxide (AlOx) thin films are highly relevant for various high efficiency silicon solar cells. In literature, AlOx layers are shown to be negatively charged dielectrics that provide an excellent passivation of lowly and highly doped p-type cSi surfaces. It is also shown in literature that high efficiency c-Si solar cells are passivated by AlOx films deposited using atomic layer deposition (ALD) and plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition (PECVD). Although several deposition techniques are mentioned in literature for AlOx deposition, solution processed AlOx thin film deposition technique is shown to be an inexpensive process.This thesis work aims to achieve excellent c-Si surface passivation by AlOx film using low cost deposition techniques. Two simple, inexpensive and non-vacuum deposition techniques — spin coating and spray coating — are investigated for surface passivation of p-type c-Si.
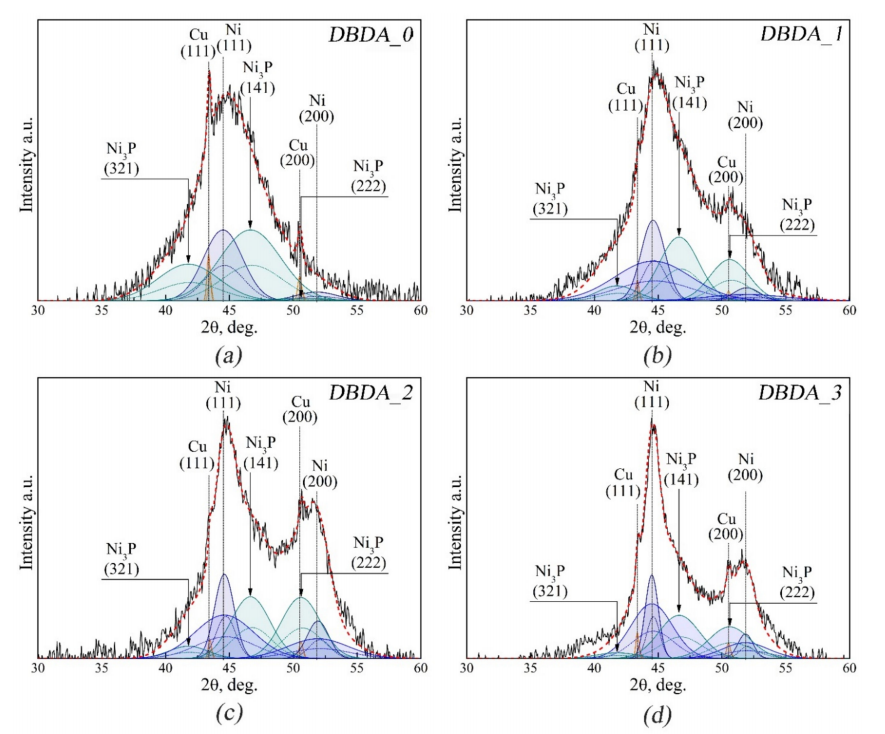
用于电路应用的有机添加剂化学镀沉积金属薄膜的制造和表征
In our work, we studied thin nickel films deposited by electroless plating for use as a barrier and seed layer in the through-silicon vias (TSV) technology. El-Ni coatings were deposited on a copper substrate from the original electrolyte and with the use of various concentrations of organic additives in the composition of the electrolyte. The surface morphology, crystal state, and phase composition of the deposited coatings were studied by SEM, AFM, and XRD methods. The El-Ni coating deposited without the use of an organic additive has an irregular topography with rare phenocrysts of globular formations of hemispherical shape and a root mean square roughness value of 13.62 nm. The phosphorus concentration in the coating is 9.78 wt.%. According to the results of the X-ray diffraction studies of El-Ni, the coating deposited without the use of an organic additive has a nanocrystalline structure with an average nickel crystallite size of 2.76 nm. The influence of the organic additive is seen in the smoothening of the samples surface. The root mean square roughness values of the El-Ni sample coatings vary within 2.09–2.70 nm. According to microanalysis data the phosphorus concentration in the developed coatings is ~4.7–6.2 wt.%. The study of the crystalline state of the deposited coatings by X-ray diffraction made it possible to detect two arrays of nanocrystallites in their structure, with average sizes of 4.8–10.3 nm and 1.3–2.6 nm.
关键词:热原子层沉积,TiN薄膜,沉积温度,P型晶体硅,表面钝化,氧化铝薄膜,化学镀沉积,金属薄膜