Introduction
Removal of photoresist materials (resist stripping) is very straightforward in theory, but can be difficult and complicated in practice. Classical methods have included SPM (sulfuric peroxide module) /piranha, ozone and UV ozone. Solvent based fluids such as n-methylpyrollidone (NMP), Acetone, Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) and Tetramethalammonium (TMAH) have all been applied to this process in various forms and combinations. Typically solvents have been combined with temperature or gases (1) to enhance throughput and reduce the damage caused by swelling in thick PR scenarios. Dynamic dispense systems have also been applied to the standard solvent combinations including aerosol sprays (2) and physical activation of the solvents through acoustic energy (3) to help reduce process times and damage induces through PR film swelling. Many dry and wet dry combinations have been implemented using various Plasma and CO2 combinations. All of the legacy methods include hazardous and toxic materials and/or high equipment expense as well as multi-step process control complexity. The stripping process becomes even more challenging by factors such as thick resist, crosslinked resist or sensitive metals or materials under the resist. This study was carried out In order to determine feasibility of the use of a unique phase-fluid based photoresiststripper in commercial semiconductor resist removal process steps. Due to their highly dynamic inner structure, phase-fluids penetrate into the polymer network of photoresists and lift the material from the surface as opposed to the surface or boundary reaction of a solvent solution. (4) As these water-based stripping fluids are non-aggressive, non-toxic, and require no special handling, the ability to apply them to industry standard resists will result in a reduction of toxic and dangerous chemistries and the environmental impact of their disposal.
This work reflects the combination of two distinct mechanisms applied to the photo resist stripping process, Phase-fluid (intelligent fluid®) and Single Wafer Megasonics. Phase-Fluid (intelligent fluid®) (4) intelligent fluids® consist of a heterogeneous mixture of two immiscible liquids that form a stable micro-emulsion. There is a balance established between the separation forces that keeps the components of the emulsion in constant motion or shape changing on a nano basis. When this very physically dynamic fluid is exposed to a film such as photo resist, the low surface energy allows for the penetration of very small gaps in the polymer surface, and the eventual forcing of the resist layer from the substrate. The film removal from the substrate is in the form of an actual physical lift-off separation and not a dissolution or etching of the film. Dilution of the Phase-Fluid is not proscribed as the equilibrium of the micro emulsion will become unbalanced and the forces will be neutralized immediately stopping any reaction. The intelligent fluid® formulas have proven to be very robust and stable in both storage time, temperature and shipment.
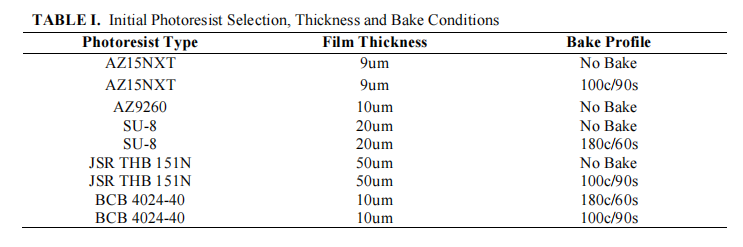
Table 2 lists the photoresists employed in the balance of this study. They are identified as PR-1 through PR-5. Five different formulations of intelligent fluids® were tested on all photoresist samples and under all process conditions. For the purpose of this study, the intelligent fluids® formulations are identified as if-A through if-E.
上一篇: 用湿化学蚀刻技术制造半导体
下一篇: 半导体晶圆键合