ABSTRACT
In recent years, photomask resist strip and cleaning technology development wassubstantially driven by the industry's need to prevent surface haze formation through theelimination of sulfuric acid and ammonium hydroxide from these processes. As a resultconventional SPM (HSO, + H,O,) was replaced with Ozone water (DIO;) for resist strippingand organic removal to eliminate chemical haze formation (1, 2]. However, it has been shownthat DIO, based strip and clean process causes oxidative degradation of photomask materials3, 4]. Such material damage can affect optical properties of functional mask layers, causingCD line-width, phase, transmission and reflection changes, adversely affecting image transferduring the Lithography process.To overcome Ozone induced surface damage, SUSS MicroTec successfulldeveloped a highly efficient strip process, where photolysis of DIO is leading to highlreactive hydroxyl radical formation, as the main contribution to hydrocarbon removal withoutsurface damage (57. This technology has been further extended to a final clean process, whichis utilizing pure DI Water for residual organic material removal during final clean (6l.Recently, SUSS MicroTec did also successfully release strip and clean processeswhich completely remove NH,OH, eliminating any chemicals known today to induce haze[7].In this paper we show the benefits of these new technologies for highly efficientsulfate and ammonum free stripping and cleaning processes.
1.INTRODUCTION
onventional resist strip processes employ a variety of steps geared towards highly effectiveremoval of organic and inorganic contamination from the mask surface.Figure 1 summarizes the process steps in mask cleaning and the mostly used chemistriesemployed in 193i mask cleaning.
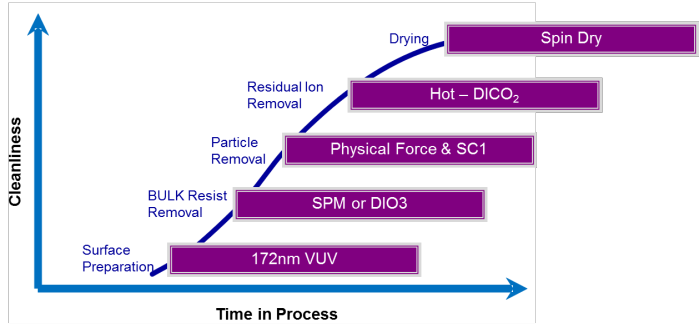
For proper wetting of the photomask surface with cleaning chemicals, higher surface energyis desired. A photomask surface is needed to be in hydrophilic state prior to the application ofwet chemistries. Hydrophilic surfaces promote better liquid distribution and uniform chemicaleffects across the surface; as part of the POR cleaning process fow a 172nm excimer VUVstep was used to achieve a low water contact-angle on the surface. The UV radiations underthe oxygen atmosphere create oxygen radicals leading to surface organic bond cleavage aswell as direct surface activation for better wetting (8,9]. However, the high energy radiationsexposure of the photomask surface may also cause interface stress or material diffusion.which eventually transforms into unpredictable mask registration shifts. Ozone water (DIO;or conventional SPM (HSO, + HO2) was used for resist stripping and organic removalhowever haze formation 10,117 or oxidative degradation of photomask materials (12, 137 hasbeen observed as a result of the very high oxidation potential of Ozone and Sulfate ionsgetting trapped on the surface and reacted with ammonium ions used in the following processsteps. Such material damage can affect optical properties of the materials and can also causeCD shift.
上一篇: 纳米压印光刻技术
下一篇: 光子晶体结构的单曝光制造