ABSTRACT: A method for transition metal sampling on the surface of as-cut and isotextured multicrystalline siliconwafers that allows quick and easy sampling without clean room environment is presented. The obtained samples wereanalysed via ICP-MS. The samples were tested for the presumably most harmful species identified from literature: AgAl, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Mo, Ni, and Ti. The method was applied to the isotexture process. The cleaning cascade after theetching was investigated and it was found that initial a-cut wafers surface contamination is reduced significatly. As-cutwafers were ident'fied as main source of contamination of the isotexture etch bath, With the help of the measuredconcentrations the enrichment of transition metals in the etch bath was simulated. Due to bleed/fed processing thecquilibrium of metal intake to the etch bath is reached after 6.000 -- 10.000 wafers. Additionally, the cleaning efriciencrof standard cleaning procedures was studied. The influence of surface contamination on the oxidation step for aSiO2/SiNx passivation stack was investigated and it was shown that surface contamination can vastly decrease theifetime of a wafer during a high temperature process.
1 INTRODUCTION
Transition metalcontaminationduring processingplays an important role concerning the quality of asemiconductor product [1l]. In contrast to the IC industryhardly any publications on surface contamination duringsolar cell processing exist. Standard IC methods forsampling of surface contaminations are hardly applicablefor solar wafers as they require polished surfaces oradvanced and expensive sampling equipment [2]Furthermore,samplingeither requires expensiveautomatedroom) equipment close to the(cleanproduction line, or the whole wafer has to be sent foranalysis, by which it is prone to the uncontrollable risk ofcontamination during transportation. Therefore a methodwas developed that allows the sampling on rough, e.gisotextured,surfaces, close to the machine, and thecontamination-free transport of the sample to an analyticlaboratory.This method was used to study the saw-damageremoval and isotexture etch process.Additionallyseveral cleaning procedures were studied and lifetimesamples were prepared to gain understanding of theimpact of surface metal contamination during a hightemperature process step.
2 EXPERIMENTAL
The first goal of the project was to develop a tailoredsampling method to extract surface contamination. Forthis purpose the Sandwich Etch sampling method wasdeveloped: The average surface concentration of twowafers is determined by pipetting 1 mL of samplingsolution onto one wafer. Another wafer is placed on top.hence a sandwich is formed. The wafers are rubbedagainst each other to ensure that the surfaces are wettedThe adhesion forces arestrong enough so that thesandwich can be handled safely. The total amount ofliquid in-between the wafers can be determined byplacing the sandwich on a balance. The sampling solutionis made up from diluted HF and H2O2. Ultrapurechemicals andwater are used due toexpected concentration of around 1 - 10 ppbw. After 10 min ofreaction time the wafers are separated and the solution iscollected using a microliter pipette and transferred to aclean PFA vessel.
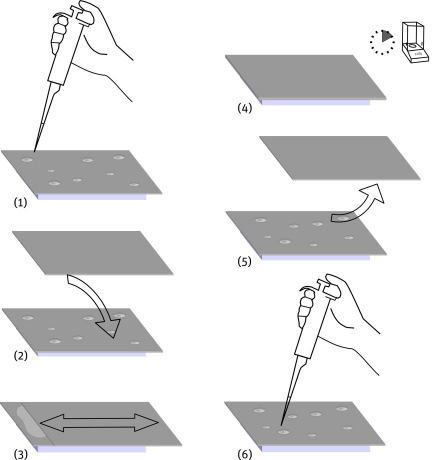
Figure 1
上一篇: InP湿法化学蚀刻-去除氧化物
下一篇: 多晶硅刻蚀方法