1. Introduction
ZnO as II-VI semiconductor material with wide band gap energy of 3.34 eV and large exciton binding energy (60 mV) at room temperature is a potential material for optoelectronic applications [1,2]. In the last two decades, ZnO nanostructures have been studied theoretically and experimentally [3–5]. Scientist and engineer believed that the specific form ZnO nanostructure has a different application [3,6]. Compared with other nanostructures, ZnO nanoparticles with the range of 100 nm have a large specific surface area and small size effect [7].. Furthermore, ZnO nanoparticles have paid considerable attention due to quantum confinement effects which control optical properties of ZnO [7,8].
In small concentrations, ZnO nanoparticles strongly inhibit the action of pathogenic microbes [13]. It also possesses antibacterial and antifungal activities [7]. Interestingly, ZnO nanoparticles have used to enhance electrochemiluminescence of luminol which used cancer biomarker detection [14]. Recently, ZnO nanoparticles are believed have a potential application as photocatalyst [11]. Even though, synthesized and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles still become major interest due to abundant their potential applications.
2. Experimental
Zinc Chloride (ZnCl2) and Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) were used as Zn precursor and for controlling pH in solution. Each of ZnCl2 and NaOH was dissolved in de-ionized (DI) water to obtained various molarities. The NaOH solution was added into ZnCl2 solution drop by drop under vigorous stirring without any heat treatment until a white suspension formed. ZnCl2 the molarities of ZnCl2/NaOH are 0.4/0.8 (ZnO-A), 0.4/0.4 (ZnO-B), and 0.8/0.4 (ZnO-C). Then, each of the suspension solutions was centrifuged to obtain precipitated of Zn(OH)2. Finally, the precipitation of Zn(OH)2 was calcined at the temperature of 400oC to obtain powder ZnO nanoparticles.
3. Results and discussion
Figure 1 (a)-(c) show SEM images of powder ZnO nanoparticles various compositions of ZnCl2/NaOH ratios. It can be observed that the ZnO nanoparticle aggregate tremendously. More clearly images of the aggregation can be confirmed in figure 1 (a). As seen from the figure 1(b) and (c), the aggregation of nanoparticles quite large. The aggregation of ZnO nanoparticles are predicted due to high surface energy of ZnO nanoparticles during calcination [15].
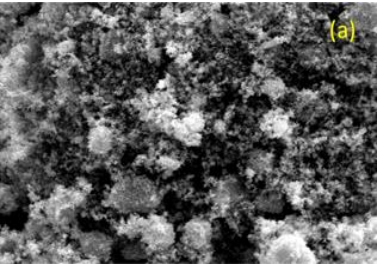
Fig1(a)
4. Conclusions
In conclusions, ZnO nanoparticles have been synthesized by using simple wet chemical method at calcination temperature of 400 oC for 2 hours. Morphologically, ZnO nanoparticles aggregated formed larger particles. Then, according to the International Center for Diffraction Data (ICDD) number #98- 002-9272, the XRD spectra confirmed that the ZnO nanoparticles have polycrystalline hexagonal structure with prefer orientation of (002) and crystallite size in the range 21 nm.
上一篇: KOH溶液中氮化铝的湿化学蚀刻
下一篇: 使用IPA溶液去除晶圆上静电荷