With the advancement in micro/nano fabrication, lm bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs) have been proposed as typical micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) piezoelectrical devices.1–4 As bulk acoustic wave (BAW) devices operating in the GHz range, FBARs have attracted much attention due to their small size, high operating frequency and potential applications in high-frequency communication and mass-sensitive sensor areas.5–8 As a kind of FBAR, solidly mounted resonators (SMRs) are composed of a piezoelectric layer sandwiched between electrodes and Bragg reector consisting of alternating high and low acoustic impedance quarter-wavelength thick dielectric or metallic layers.9,10 The SMR, with good mechanical strength and excellent acoustic properties, and being closer to CMOS integration, was therefore chosen in this work.11,12.
In recent decades, owing to excellent piezoelectric property, better quality factor, and high electromechanical coupling coeffiffifficient, ZnO is becoming a very promising candidate for FBAR devices as a piezoelectric material.13–16 However, ZnO have the drawback of low longitudinal acoustic wave velocity and low resistance, which limits its application to high sensitivity acoustic sensors.17 MgXZn1 XO, a ternary compound formed by alloying ZnO and MgO, has attracted more and more attention due to its special properties such as higher acoustic velocity and resistance than that of ZnO.18–20 Studies have shown Mg2+ is doped into the ZnO crystal by substituting the Zn2+ position and MgXZn1 XO still maintains the wurtzite crystal structure when the percentage of Mg atoms is less than 33%.21 By controlling the percentage of Mg-doped in the material, the MgXZn1 XO lms with satisfactory sound velocity and electromechanical coupling coeffiffifficient can be tailored.
In this paper, we fabricated MgXZn1 XO lms with high c-axis orientation by RF magnetron sputtering and characterized structure and surface morphology of MgXZn1 XO lms. In addition, we explored the effffects of FeCl3$6H2O as a novel etchant on surface morphology, optical transmittance and shape control of MgXZn1 XO lms. The novel Bragg acoustic reector, made entirely of metal, has small internal stress and good heat conduction. We fabricated a SMR based on MgXZn1 XO lms and Bragg acoustic reector with the optimized fabrication condition and investigated the performance of SMR.
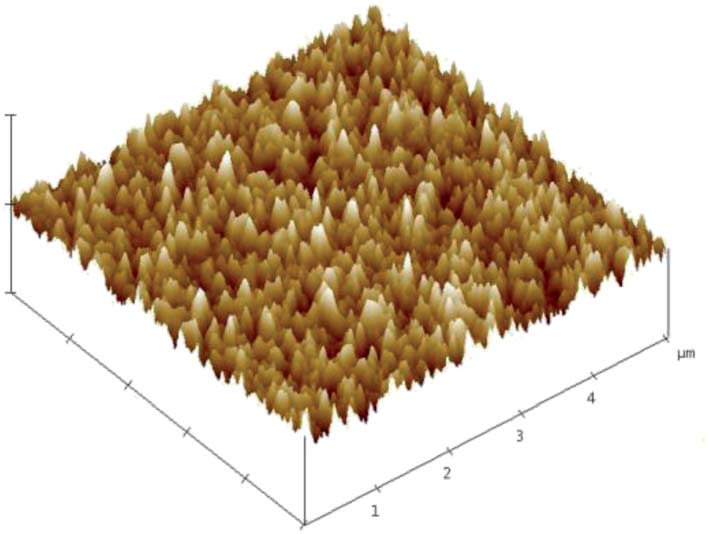
Fig3
Fig. 3 shows a three-dimensional AFM image of the MgXZn1XOlms deposited on silicon substrate. The surface roughness of the MgXZn1 XO lms is 3.37 nm. The rounded and homogeneous grain shape can be observed from the picture, which reveals the fact that MgXZn1 XO lms with a homogeneous smooth surface over the whole wafer. Low surface roughness is connected with low acoustic loss in MgXZn1 XO lms, which is suitable for SMR.
The SEM micrographs of surface texture MgXZn1XOlms etched in difffferent etchants were illustrated in Fig. 5. The concentration of all etchants was controlled to be 0.01 mol l 1 and the etching time was controlled in 1 min. It is observed clearly that the etched samples show distinctive rough surface morphologies due to difffferent etching rates of difffferent etchants. The sample as-grown MgXZn1 XO lms without etched consists of close-packed hummock-like crystals surface morphology with smooth, homogeneous and uncracked. By compared, hummocklike crystals are becoming gradually disappeared and the surfaces are becoming gradually rough and cracked with the increase of etching rate in difffferent etchant solutions. It can be proved that surface texture of MgXZn1 XO lms is the most severely damaged in HCl solution, the least damaged in C2H4O2 solution, and the moderate in FeCl3$6H2O solution.
上一篇: 独立晶片表面颗粒沉积的数值分析
下一篇: 通过在玻璃上旋涂的低温晶圆键合