Displays based on inorganic light-emitting diodes (LED) are considered as the most promising one among the display technologies for the next-generation. The chip for LED display bears similar features to those currently in use for general lighting, but it size is shrunk to below 200 microns. Thus, the advantages of high effificiency and long life span of conventional LED chips are inherited by miniaturized ones. As the size gets smaller, the resolution enhances, but at the expense of elevating the complexity of fabrication. In this review, we introduce two sorts of inorganic LED displays, namely relatively large and small varieties. The mini-LEDs with chip sizes ranging from 100 to 200 µm have already been commercialized for backlight sources in consumer electronics applications. The realized local diming can greatly improve the contrast ratio at relatively low energy consumptions. The micro-LEDs with chip size less than 100 µm, still remain in the laboratory. The full-color solution, one of the key technologies along with its three main components, red, green, and blue chips, as well color conversion, and optical lens synthesis, are introduced in detail. Moreover, this review provides an account for contemporary technologies as well as a clear view of inorganic and miniaturized LED displays for the display community.
According to the Research and Markets, a market research institution, the global micro-LED display market is predicted to soar from USD 0.6 billion in 2019 to USD 20.5 billion in 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of about 80% . The main reason for the market outbreak is the sharp increase in demand for brighter and more energy-effificient display panels, needed for surging devices such as smart watches, mobile phones, TVs, laptops, augmented reality (AR) and VR. According to Yole’s optimistic estimate, the market of micro-LED display will reach 330 million units by 2025 (Figure 1) . Although the prospects of market are highly optimistic at present, micro-LED displays still face technological challenges, especially in the cases for which some key technologies and process equipment have not yet been made suffificiently developed. Therefore, the relatively mature mini-LED is expected to be the fifirst commercialized variety while the micro-LED display technology is still in its nascent state.
High dynamic range (HDR) is one of the important features for next generation displays. To achieve HDR with contrast ratio (CR) higher than 100000:1, high peak brightness and excellent dark state of the display system are simultaneously required. Although the best requirement for HDR is pixel level dimming, which is described as micro-LED technology, there are still some technological bottlenecks that make micro-LED harder to realize quick commercialization. Therefore, a compromising way to realize multi-zone local dimming for LCD is direct-lit mini-LED backlight. Mini-LED technology has much smaller size of LED, which means it can divide more dimming blocks in a certain size LED backlight. Recently, LED manufacturers have turned to research and develop mini-LED. Most of existing processes and equipment for conventional LED can be used continuously for fabrication of mini-LED.
Tan et al. discussed the system modeling and performance evaluation of LCDs with mini-LED backlight [18]. First, a model of LCD system with a direct-lit mini-LED backlight is set up for simulation (Figure 2). The backlight unit consists of square-shaped mini-LED array. A diffuser plate is utilized to widen both spatial and angular distributions, and a liquid crystal (LC) panel is applied to control the output light. The parameters of the model, such as p, s, H1, and H2, are based on the device confifiguration reported in Reference. To validate the model, four patterns are used to simulate the dynamic CR of the model, and the simulated results can agree with the measured data from Reference reasonably well.
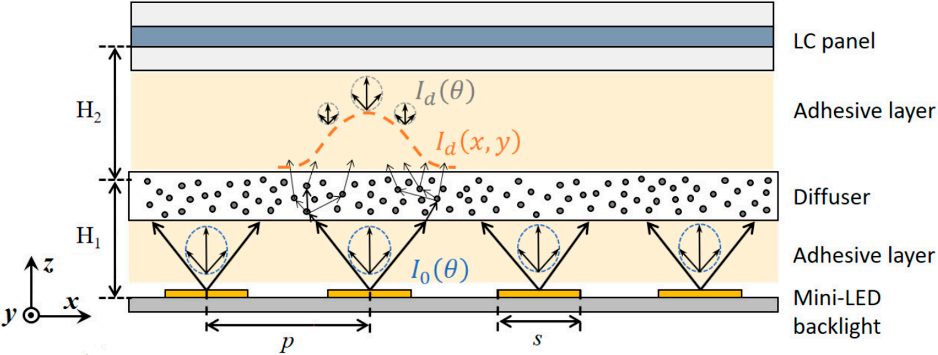
Fig1
Then, a subjective experiment is designed and carried out to determine the human visual perception limit of halo effect. The LabPSNR, an evaluation metric used to quantify the difference between displayed image and target image, should be larger than 47.4 dB. Based on this limit, the requirement of local dimming zone number can be proposed: over 200 local dimming zones for high CR ≈ 5000:1 LCD panels and more than 3000 dimming zones for CR ≈ 2000:1 LCDs (Figure 4).
Dl, a Japanese manufacturer, demonstrated an automotive central control panel based on a16.7 inch curved screen with a straight down type mini-LED backlight at 2018 SID Display Weekshown in Figure 7a. The contrast and color of the screen can be presented perfectly even incomplex situations because of the local dimming with 104 dimming zones in the screen. BOE, one ofthe largest display makers in China, exhibited a 27-inch ultra-high-definition (UHD) panel, which useda mini-LED backlight with 1000 local dimming zones. Its brightness is up to 600 nits and its contrast isup to 1,000,000:1. In addition, BOE also showed a 5.9-inch mobile phone panel which was only 1.4 mmin thickness, shown in Figure 7b.