The ability to chemically characterize the contamination on silicon wafers is of critical importance to the semiconductor industry. It provides information on possible unwanted chemical processes taking place on the wafer surface and helps in determining the true source of the contamination problem. This type of information is not readily accessible with standard laboratory equipment. Synchrotron radiation-induced total reflflection X-ray flfluorescence (SR-TXRF) was combined with X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) to determine the chemical state of Fe contaminations on a silicon wafer surface. Main purpose of the study was to test the method for a contamination issue as it could appear in a microelectronic VLSI production fab.
Iron contaminations on the surface of Si wafers are known to be a serious limiting factor to yield and reliability of complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) based integrated circuits. Total reflflection X-ray flfluorescence (TXRF) is a widespread analytical technique for the monitoring of surface contamination on nonpatterned wafers in the semiconductor industry. In laboratory-based instruments it offers detection limits down to the 5E9 at/cm2. When higher sensitivity is requested, monitoring is typically carried out by vapor phase decomposition (VPD) of the native oxide layer and analysis by means of laboratory-based TXRF and/or inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) on the expense of the loss of the information relative to the location and distribution of the contamination on the wafer. For tracing the source of the contamination not only the distribution of the contamination is very valuable but also additional information on the chemical state of the element can be helpful.Understanding the chemical state is important to gain information on the source of contamination: if more metallic in nature the contamination could be particles from wear or shearing of moving parts; if the iron is an oxide, corrosion may be taking place. Other species may indicate unexpected chemical reactions, which take place.
Synchrotron radiation-induced TXRF (SR-TXRF) is a microanalytical technique which offers sensitivities as high as 8000 cps/ng and detection limits in the fg range for transition metals with a multilayer monochromator and a bending magnet beamline.With a crystal monochromator the technique can be coupled to X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) to gain information on the chemical environment of the specifific elements of interest. With this modifified setup there is a flflux reduction of about two orders of magnitude, but it is still suffificient for X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) analysis at ppb level.
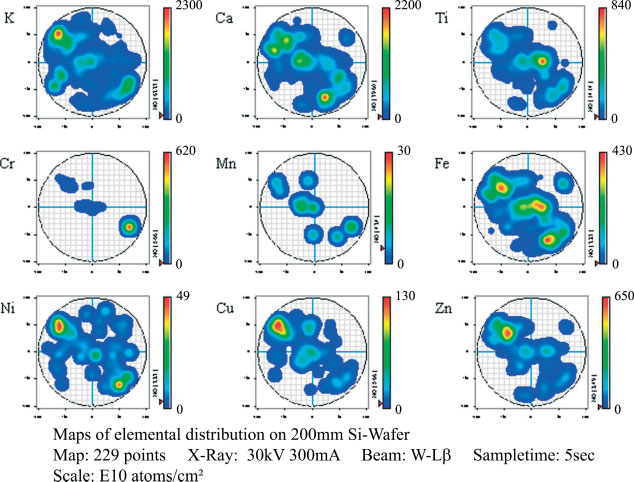
Fig1
A Si wafer from IBM laboratories showing surface contaminations in the 4E12 at/cm2 rangefor Fe has been investigated. The contaminations were not intentionally prepared, but real contaminations due to fabrication processes. SR-TXRF XANES measurements were performed at the bending magnet beamline L at HASYLAB using a modifified micro-XRF setup. This modifified setup allowed TXRF measurements with scanning capability. The Wafer with 200 mm diameter was mounted vertically on a custom-made holder on a x,y,z,θ-stage in front of the side-looking detector to allow area scans and scans over the angle of incidence. The distance between sample and detector was set to 1 mm. A laminar flflow hood is present on the setup at HASYLAB to prevent contamination during the measurement. The Si(111) double crystal monochromator was used and a silicon drift detector (SDD) with 50 mm2 active area (VORTEX 50 mm2, Radiant Detector Technologies) for the detection of the flfluorescence radiation. The beam dimensions were adjusted to 1600 × 400 µm (vertical × horizontal). All measurements were performed in air.
Figure 1 shows the contamination maps on the 200-mm Si wafer obtained with a laboratory TXRF instrument; three areas are marked and labeled (A5, A7, and A21). The TXRF instrument is a Rigaku TXRF 300 3 crystal system with an 18-kW generator. The system can measure K line series for elements from Na, Al, and Mg through the transition series to heavy elements such as Mo. For quantifification the instrument was calibrated with a reference standard sample provided by the manufacturer. The strength of the instrument is the full-wafer-mapping software which was designed as a fast analysis highlighting very high points or repeatable patterns of contamination. There are several papers on the statistics of the analysis.
上一篇: 一种用于聚集晶圆芯片电气故障的创新方法