QLED TV is a new television technology that is taking many of its cues from OLED TV technology. It consists of extremely small light-emitting crystals called quantum dots. Most TVs today including all of those made by companies and just about every other TV brand are based on decades-old LCD, or liquid crystal display, technology. In the past few years’ Better technology and more advanced manufactured, called OLED or organic light-emitting diode. OLED TVs have the best picture quality we've ever tested, keeping LCD-only companies from achieving the coveted top positions on certain lists. At the moment a new TV display technology on the horizon called QLED, and it might be even better than OLED and LED. Short for "quantum dot light emitting devices," QLED has the potential to match the infinite contrast ratio of OLED, with better power efficiency, better color and more .In this article we will discuss about the QLED and OLED display technology.
Quantum Dot is composed of semiconductor materials which look like a nanocrystal sphere. These nanocrystals emit light with absorbing light due to flow of electric current. The lightning wavelength differs depending on the dot size. LCD alone is not capable of emitting its own light. There should be a light source or backlight. A LED backlight used the three basic colors-blue, green, and red in order to come up with a white color light. Recently, one of the popular LED LCD colors is blue coated with a yellowish phosphor to achieve a white light color and QD LED TV is found as a more advanced version of this. The manufacturer no longer used the blue LED with yellowish phospor, but instead they use QD particles for achieving white color. The QDLED absorbs the emitted blue light then transfer it to red and green to creating the desired white color. This process is also known for achieving an accurate LED colors. OLED is composed of organic molecules made of thin films that create light with the use of electricity. This type of lightning technology is capable of creating crisper and brighter displays on electronic devices than the traditional liquid crystal displays (LCD) and light emitting diodes (LED).
Meanwhile, the Organic Light-emitting Diode (OLED) display is made of organic compound which releases light with the presence of an electric current. The pixel is capable of emitting light on its own. It only means that this type of LED display have no issues regarding backlight leaking. Thus, Organic Light-emitting Diode is different from Quantum Dot Light-emitting Diode in terms of in expressing colors. QD LED uses LCD-based technology which is slightly difficult to consider as the next generation display. However, OLED is considered as the next generation display which is transparent, flexible and roll-able. It has relatively low processing temperature suited for a plastic substrate when you wish to make a flexible display and because it does not require a backlight as compared to QD, it can be optimized in creating a transparent generation display.
QLED means Quantum dot light emitting diodes and are a form of light emitting technology and consist of nano-scale crystals that can provide an alternative for applications such as display technology. The structure of a QLED is very similar to the OLED technology. But the difference is that the light emitting centers are cadmium selenide (CdSe) nanocrystals, or quantum dots. A layer of cadmium-selenium quantum dots is sandwiched between layers of electron-transporting and holetransporting organic materials. An applied electric field causes electrons and holes to move into the quantum dot layer, where they are captured in the quantum dot and recombine, and emitting photons. The spectrum of photon emission is narrow, characterized by its full width at half the maximum value. There are two major fabrication techniques for QD-LED, called phase separation and contactprinting. QLEDs are a reliable, energy efficient, tunable color solution for display and lighting applications that reduce manufacturing costs, while employing ultra-thin, transparent or flexible materials.
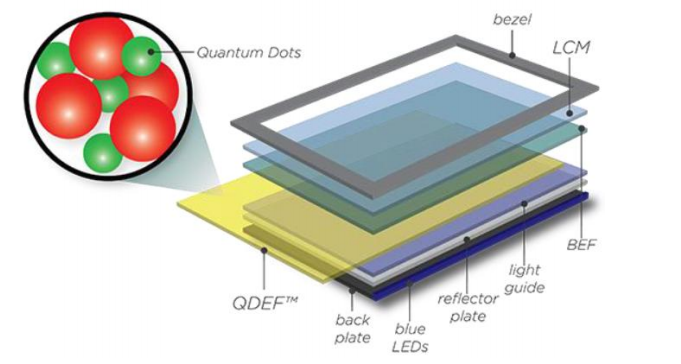
Fig1
Quantum Dot (QD) displays are quite different as the technology is based on small conducting nanocrystals, usually in the range of 2 to 10 nanometers in diameter. The color of light produced or filtered by a dot is based on its diameter and using a few of these could produce all your necessary colors. Like OLED, light and colors could be supplied on demand and QD-LEDs can be very bright. However, current QD displays are based on a blue LED backlight which is then filtered to a white light before passing through the familiar LCD color producing layer.
Color gamut is seen as one of OLED’s big advantages over LCD, allowing for more vivid viewing experiences and accurate color reproduction, so long as the media also supports it. LCDs often fall short on color accuracy and gamut because of their reliance on a pseudo-white backlight (this is made from blue LEDs with a yellow phosphor coating). However, the highly accurate nature of Quantum Dots means that developers can use a pure blue back light and accurate red and green filters produce a true white light, which can then be filtered into better looking colors.
上一篇: 量子点发光二极管:结构、机理和制备
下一篇: 量子点溶剂对QLED性能的影响