The copper end paste used in multilayer ceramic capacitors sintered in nitrogen atmosphere will lead to carbon residue of organic vehicle, which will lead to the reduction of electrode conductivity and high scrap rate. With an attempt to leave no residue in the sintering, the compatibility of solvents and thickeners should be improved because it has an important influence on the hierarchical volatilization and carbon residue of organic vehicles. In this work, the volatility of different solvents was compared and several solvents were mixed in a definite proportion to prepare an organic vehicle with polyacrylate resins. The hierarchical volatility and solubility parameters of mixed solvents were adjusted effectively by changing proportions of different components, the thermogravimetric curves of resins and organic vehicles were measured by thermogravimetric analyzer, the effect of solubility parameter on the dissolvability of resins in the solvent and the residual of organic vehicles were studied. Results showed that the hierarchical volatilization of solvents can be obtained by mixing different solvents; the intrinsic viscosity of the organic vehicle is higher and the thermal decomposition residue of polyacrylate resins is lower when the solubility parameters of mixed solvents and polyacrylate resins are closer. The low residual sintering of organic vehicles can be achieved by using the mixed solvent with hierarchical volatility and approximate solubility parameters as resins.
With the increasing demand for multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCC) in the market, the requirements of electronic information products for MLCC tend to be high frequency, low power consumption, miniaturization, superior energy storage and low cost. It is worth mentioning that the copper end electronic paste is composed of three main components including conductive phase (copper), bonding phase (glass or oxide crystals) and organic vehicle. The organic vehicle consists of organic solvent and thickener, in which the organic solvent accounts for 65-98%. In addition, polyacrylate resin is commonly used as the thickener in the organic carrier and the sintering residue of the organic vehicle mainly depends on the thermal degradation of the polyacrylate resin thickener in the solvent. At present, Cu electrode with better conductivity has replaced precious metal electrode as the mainstream electrode material, however, due to the oxidation characteristics of Cu, sintering can only be performed in nitrogen. Carbon residue caused by sintering Cu end slurry in nitrogen atmosphere poses a great challenge to the selection of organic vehicle composition of base metal inner electrode multilayer ceramic capacitor (BME-MLCC). The residual rate of thickener in organic vehicles is the key factor to determine the conductivity of electrodes. The carbon remaining in the conductive film will greatly affect the electroconductibility of the film. There are copious studies on the effects of sintering atmosphere, temperature, rate, and time on electroconductibility , but there is still not clear to our knowledge on the effect of thermal degradation characteristics of thickener on carbon residue, and thickener is the main component of the organic vehicle that applied in MLCC. Therefore, it has practical significance to develop the methods to select the mixed solvent with hierarchical volatility and to prepare organic vehicles with extremely low residue, on the basis of the relationship between the mutual solubility of mixed solvents and thickeners.
The organic vehicle is generally composed of solvent, thickener, surfactant, thixotropic agent, and other additives. The organic solvent is the primary component of the organic vehicle, with about 65% – 98% of the total mass of the organic vehicle. It should dissolve the thickener quickly with excellent solubility and have a high boiling point to avoid volatilization in preparing the organic vehicle. The organic vehicle with mixed solvent can adjust the volatilization characteristics and achieve non-volatilization at low temperature, whereas hierarchical volatilization at drying temperature. Meanwhile, it can improve the viscosity and fluidity of slurry, and enhance its stability and printability. In addition, the reasonable selection of mixed solvents can also enhance the solubility of thickener and the wettability of copper, which greatly improves the performance of electronic paste in MLCC.
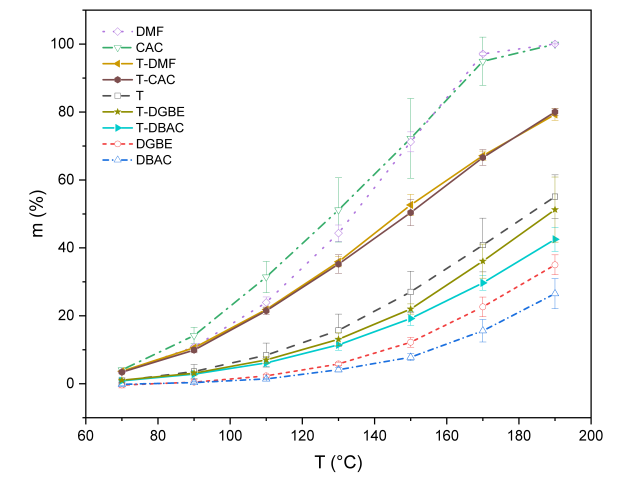
Fig1
It is an effective method to adjust volatilization by combining solvents with different boiling points. This can be attributed to the partial pressure of the mixed solvent. According to Henry’s law, under a certain temperature and equilibrium state, the relative content of the mixed solvent determines the relative ratio of vapor pressure. The ratios of the four mixed solvents are consistent before the thermal volatilization. In the process of thermal volatilization of T-DMF and T-CAC, the two solvents with low boiling points (DMF and CAC) will volatilize preferentially at low temperatures, however, T has less volatilization at low temperatures. Different volatilization rates result in the increased relative ratio of T to DMF and CAC after volatilization for a period, the partial pressure of T increases while the partial pressure of DMF and CAC decreases, which will cause more volatilization of T. For T-DGBE and T-DBAC, T is the component with a low boiling point and volatilizes mainly at the beginning. With the change of partial pressure, the volatilization of DGBE and DBAC will be increased. Therefore, mixed solvents with proper proportions can achieve hierarchical volatilization in order to avoid volatilization unevenly.