In this work, ZnO films were deposited by Direct Current (DC) magnetron sputtering, on polished silicon substrate Si(100) (non-etched), etched for 1 min, 5 min, 10 min and 15 min. The etching of the substrate was carried out by means of dry plasma at different time and they compared with non-etched substrates. Etched silicon substrate effect on the structural and morphological properties of ZnO films was examined, and a new nanostructure can be obtained by the modification in morphology of ZnO film, and this will obviously useful for the electrical and gas sensitivity applications. AFM have been used to investigate the morphology and the roughness behaviors of ZnO films growth on etched and non-etched silicon substrates. SEM images for the Si(100) etched and non-etched effectuated with two modes (surface top view and cross section), the SEM was used too for ZnO film deposited on etched substrate (the etched time increase from 1 to 15 min) and non-etched Si substrates.
En este trabajo, las películas de ZnO se depositaron mediante pulverización catódica con magnetrón de corriente continua (DC), sobre sustrato de silicio pulido Si(100) (sin grabar), grabado durante 1 min, 5 min, 10 min y 15 min. El grabado del sustrato se realizó mediante plasma seco a diferentes tiempos y se compararon con sustratos no grabados. Se examinó el efecto del sustrato de silicio grabado en las propiedades estructurales y morfológicas de las películas de ZnO, y se puede obtener una nueva nanoestructura mediante la modificación de la morfología de la película de ZnO, y esto obviamente será útil para las aplicaciones de sensibilidad eléctrica y de gas. AFM se ha utilizado para investigar la morfología y los comportamientos de rugosidad del crecimiento de películas de ZnO en sustratos de silicio grabados y no grabados. Imágenes SEM para el Si(100) grabado y no grabado efectuado con dos modos (vista superior de la superficie y sección transversal), el SEM se usó también para la película de ZnO depositada en el sustrato grabado (el tiempo de grabado aumentó de 1 a 15 min) y Sustratos de Si no grabados. Se emplearon técnicas de espectroscopía de fotoelectrones de rayos X (XPS) y difracción de rayos X (XRD) para investigar el contenido de elementos de las películas de ZnO y las propiedades cristalográficas, respectivamente. Además, se estudió la variación de los datos del ángulo de contacto con el agua (WCA) relacionados con la rugosidad de las películas de ZnO depositadas sobre sustrato de Si grabado en diferentes tiempos.
DC magnetron sputtering set up was utilized to deposit thin ZnO film on Si(100) substrate (etched and nonetched) using ZnO Target. The power was 100 w and deposition time was 7 min and the deposition rate was about 17 nm/min. The T chamber is home-made, it was manufactured from SS316, the residual pressure was 1x10 -6 Torr and the working pressure was 7 mTorr at room temperature. The description of the vacuum system was cited in details in previous work [23]. PECDV dry plasma used to etch the Si(100) substrate at several times (etched times were 1min, 5 min, 10 min and 15 min) using SF6 plasma.
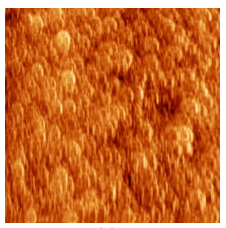
Fig1
The ZnO film became more porous with increasing the etched time (for 10 min etching time) and as consequence the robin became longer (more black zone indicates to bottom) and higher (their diameter of aggregate or wires varied from 500 nm to 1µm ) as shown in Figures (4-e) and (4-f) where the SEM images for top surface at 25 k and 50 k magnification, respectively. Similarly, there are higher and longer robins whose length varied form 1 µm to 4 µm for ZnO film deposited on etched Si(100) for 15 min, as shown in the Figures (4-g) and (4-h) corresponding to top view SEM images at 25 k and 50 k magnifications, respectively.
下一篇: 通过晶体硅微加工形成横向分形