This study investigated the degree of phase transformation, surface roughness, and bond strength of zirconia immersed for various times in a 40% hydrofluoric acid (HF) solution. Non-etched sintered zirconia specimens were used as the control, while experimental groups were etched with a 40% HF solution for 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160 and 320 min. In each of the control and experimental groups, five specimens for X-ray diffraction analysis, four for surface morphology and surface roughness analysis, and ten for bonding strength measurement were used. As a result, the surface roughness of zirconia increased as the application time increased during the 40% HF etching, but the bond strength between zirconia and resin cement did not increase proportionally. The phase transformation from tetragonal to monoclinic also gradually increased with application time.
INTRODUCTION
Zirconia widely used as a restorative material in clinical practice is yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal (Y-TZP), which is a non-metallic material used in dentistry due to its excellent mechanical properties and aesthetics1,2). Attempts to increase the bond strength of resin cement to zirconia and to improve the quality of adhesion between the two interfaces are still in progress. In most clinical cases, the surface roughness of zirconia is increased by air-borne abrasion using Al2O3, and then chemical bonding is induced by bonding with resin cement containing 10-methacryloyloxydecyl dihydrogen phosphate (MDP)3-5). However, there is a limit to the bond strength that can be obtained through this method6,7). To improve this, several studies8,9) are being conducted to strengthen the bonding force through mechanical bonding. Until recently, it was recognized that acid etching the zirconia surface using hydrofluoric acid (HF) was nearly impossible. Recent studies10,11), however, have reported improvements in bond strength by treating the zirconia surface with HF at various concentrations and temperatures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Zirconia specimens (NexxZr T, Sagemax, Federal Way, WA, USA) were prepared for X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, surface roughness analysis, and shear bond strength (SBS) measurements. Zirconia specimens took the form of standard cylinders with a diameter of 12 mm and a height of 8 mm, and were prepared by CAD/CAM milling and sintering. The materials used in this study are listed in Table 1.
RESULTS
XRD analysis
The XRD patterns of the zirconia surfaces from the control group and 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160 and 320 min HF treatment groups are shown in Fig. 1. Figure 2 highlights the mean monoclinic phase content (Fm) values with the standard deviation of the zirconia in the control group and each of the experimental groups.
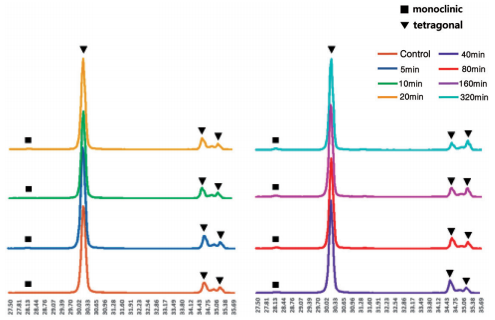
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of zirconia surfaces treated with control and 40% HF for 5, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160 and 320 min, respectively. At 2θ of 28.2°, the monoclinic (−111) peak was detected on the zirconia surface of the control group and all experimental groups.
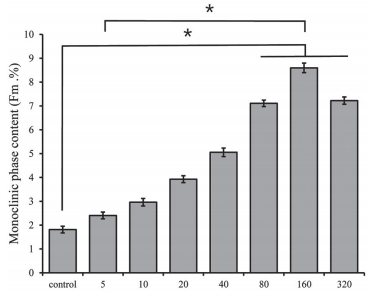
Fig. 2 Mean monoclinic phase content (Fm) values of the zirconia surfaces in the control and 40% HF treated groups. *means that there is statistical significance between the control group and the experimental groups or between the experimental groups (p<0.05).
The monoclinic phase structure was detected on zirconia surfaces in all groups, and the monoclinic (−111) peak was detected at a 2 theta of 28.2o . The monoclinic crystal phase in the control group was the lowest, and as immersion time increased monoclinic phase content (Fm. %) tended to gradually increase, with the exception of the 320 min HF treatment group. The corresponding value in the 160 min HF treatment group was the highest. Although there was no statistical significance, the monoclinic phase content was lower in the 320 min HF treatment group than in the 160 min HF treatment group.
SBS test
Mean bond strength values with standard deviations are presented in Fig. 6. SBS values showed a completely different tendency from the monoclinic phase content, mean Ra values, and SEM images. The SBS of the 5-min HF treatment group was significantly higher than that of the control group, just as the SBS of the 10-min HF treatment group was significantly higher than that of the 5-min HF treatment group. However, no statistically significant differences were found between the 10, 20, 40, 80, 160, and 320 min HF treatment groups. In short, SBS increased significantly for up to 10 min of immersion, after which it was maintained at a constant value.
DISCUSSIONS
In most studies concerning zirconia etching with an HF solution, etching has occurred only for a relatively short time of 5 to 10 min12,16). This practice seems to be derived from the etching time associated with the use of lowconcentration HF for conventional ceramic materials. However, according to Flamant et al. 18), a concentration of 40% and less than 2 h of etching time are in fact the most suitable conditions for HF etching of the zirconia surface.
CONCLUSIONS
It is concluded that 10 min of the immersion time is the optimal for 40% HF etching on the zirconia surface at room temperature. The mechanical properties of the HF-etched zirconia surface greatly depend on whether the phase transformation from tetragonal to monoclinic acts as a toughening or a degradation mechanism.