Introduction: Inkjet piezoelectric printing technology has an important position in many fifields of printing technology for its excellent property [1, 2]. Its application has expanded from conventional graphic printing to new areas such as electronics [3–5], drug dose deployment [6] and cell printing [7, 8]. As an indispensable piezoelectric component, the processing quality of lead zirconate titanate (PZT) membrane will affect the whole actuating property and inkjet performance [9]. The piezoelectric membrane was prepared by sol–gel methods [10, 11], so the quality of platinum (Pt) substrate property is vital to ensure membrane quality. In addition, the bottom electrode substrate has a great inflfluence on the grain and nucleation of PZT growth which affect piezoelectric property seriously. The pattern process is always required in Pt thin-fifilms before the fabrication of PZT, and we use simple fabrication protocol for wet etching Pt thin-fifilm in boiled aqua regia [12]. In general, the negative photoresist was used as mask for its good anti-etching characteristic. However, the phenomenon of scum is common in negative photoresist and the strong oxidation and corrosion of aqua regia will partly etch photoresist, even resulting in denaturation which increases the diffificulty of scums removal. The scums in the substrate cause a large number of black spots in the subsequent spin-coated PZT, which results in decreased piezoelectric property, poor adhesion of substrate and inadequate feature size control. So the removal of photoresist of Pt surface is the key to the manufacturing process of PZT.
In the photolithography, the short-chain molecules in the photoresist are developed and the long-chain molecules remain in the substrate. Respectively, the short-chain molecule can be completely removed in the development, while the long-chain molecule has some scums after removal of photoresist. Therefore, the short-chain molecule in the photoresist is more easily removed and has less scum. A double-layer resist method was employed in this Letter, and the positive photoresist easily removed was chosen as the bottom layer, negative photoresist as the top layer. After the top layer exposure, the short-chain molecule in the top layer was crosslinked to the long-chain molecule, and the long-chain molecule in the bottom layer was broken to the short-chain molecule. Hence, the bottom layer is more easily removed. The double-layer resist method can remove the scum in the substrate effectively. These scums can cause the poor quality of the subsequent thin fifilm or the ‘grass’ during dry etching [26]. Therefore, the complete removal of photoresist is critical in order to obtain clean surface quality of substrate during the dry and wet etching process. Generally, this method can be widely used in the removal process of negative photoresist clearly on various bases where the very clean surface is required.
Results and discussions: This method has an excellent descum result on the double-layer resist coating areas. The photoresist type and spin speed of positive photoresist have a decisive inflfluence on the fifinal property of the substrate. Distribution of the scum is uneven and random. To quantify the cleanliness of the Pt surface, the mean number of scum, defifined as the ratio of the total number of scum at 20 mm2 to the area of 20 mm2 , is set as the standard in this Letter.
In this experiment, although AZ50XT was used as the bottom layer resist, the top layer resist was lifted and patterns deformed seriously in the negative photoresist development process, as shown in Fig. 2a. As the thickness of AZ50XT (15.40 μm) is much higher than BN308 (7.06 μm), the bottom layer resist cannot be covered completely by the top layer resist and the fracture of the top layer resist happens. The stripper and acetone entered and then dissolved the bottom layer resist in the subsequent development, which caused the deformation of patterns.
As shown in Fig. 2, the black wrinkle appeared in all three cases, which was due to the fact that the organic solvent in the developer enters the molecular chain of resist, causing the swell of negative photoresist [27], particularly in the double resist area. Due to the poor adhesion of the double resist, the top layer is separated from the bottom layer. However, the resist does not break the strong cross-link of negative photoresist. The redundant developer was cleaned by detergent, and the double resist is bonded again. The air between the double-layer resist was sealed inside, so some wrinkles appeared inevitably. Though the wrinkle existed in the area of double-layer resist, experiment proved that it has no impact on the pattern of Pt in the boiled aqua regia. Therefore, AZ703 with low viscosity was chosen as the bottom layer resist.
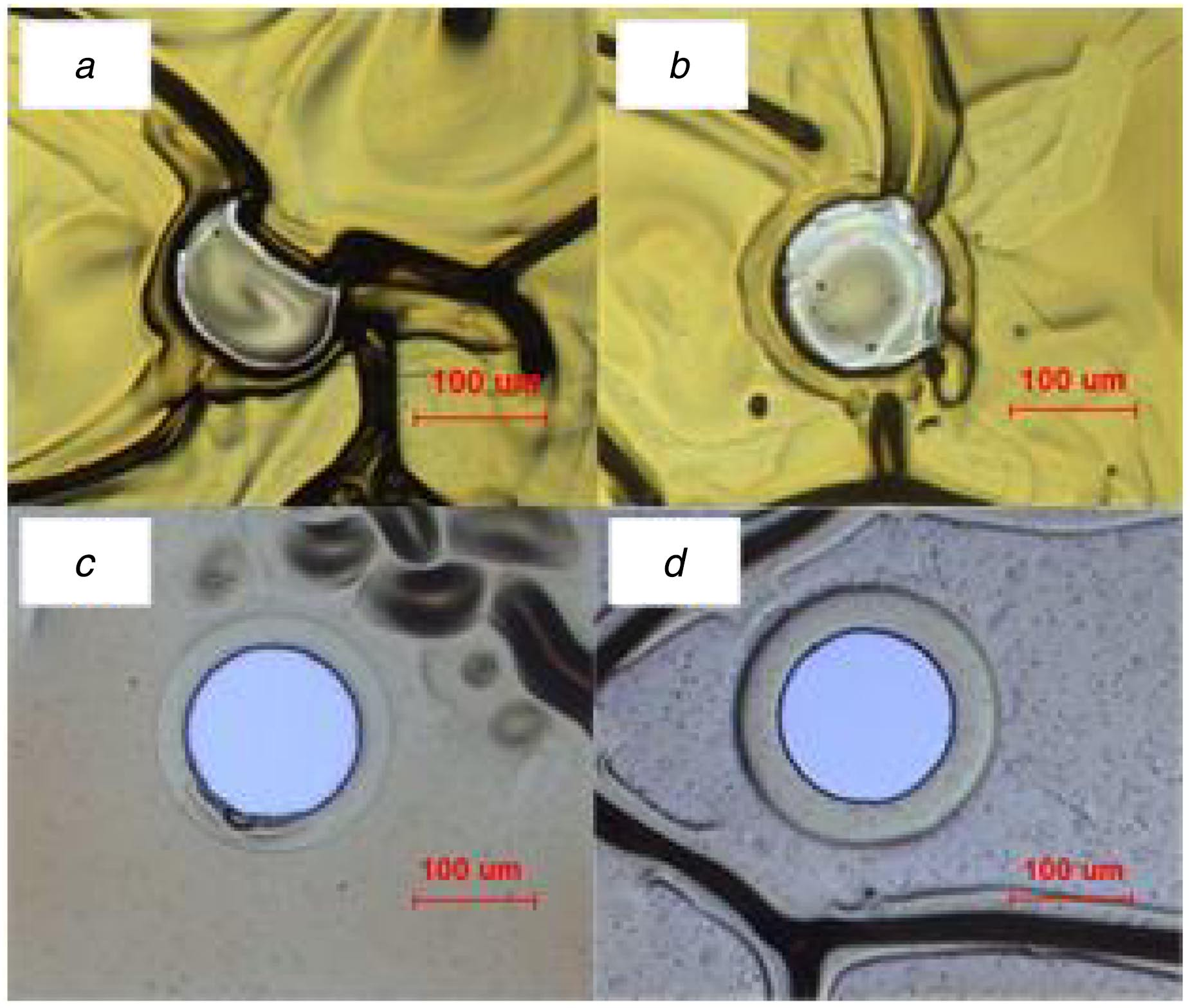
Fig1
A circular pattern with a radius of 100 μm is designed. The bottom layer resist will gradually retract from 0 to 8 μm by step-size 1 μm. As shown in Fig. 5, when d is 0 μm, the pattern completely deformed. The bottom layer sidewall is exposed to the stripper and acetone, and then the solvent enters the wrinkling area, leading to deformation. When d is <4 μm and >0 μm, the pattern also completely deformed. Due to the swell effect of negative photoresist, the resist has a 2–3 μm deformation. The solvent will also enter the resist by means of the little deformation. When d is <8 μm and >4 μm, the pattern has different degrees of deformation. As the contact area between negative photoresist and substrate is not big enough, the bonding force is insuffificient to sustain swell of the whole top layer. When d reaches 8 μm, the pattern performs well and has no deformed circle appears. Therefore, to obtain maximum coverage of the bottom layer resist, 8 μm is chosen as the optimal retraction distance of the bottom layer. Of course, the mask needs to be retracted 8 μm on the edge of the silicon wafer to guarantee that the whole wafer is shrouded by negative photoresist.
上一篇: 光刻胶溶解过程中表面粗糙度的变化
下一篇: 过氧化氢对铜抛光的影响