Experimental
Copper slurry preparation.— In this study, a hydrogen peroxide semiconductor grade, 30 wt % based slurry was used to perform etching and polishing tests. -alumina Degussa, 99.99%, primary particle size 13 nm particles were used for the slurry preparation. As a complexing agent, citric acid C6H8O7, pK1 = 5.8, pK2 = 4.3, pK3 = 2.9 , a common tricarboxylic acid, was selected and purchased from Aldrich Co. NH4OH semiconductor grade, 28 wt % was used to adjust slurry pH. The oxidant was mixed into slurry just before the polishing test to prevent possible H2O2 decomposition. For slurry preparation, a mechanical agitator was used for 5 min at 20000 rpm.
Surface characterization methods.— Cu wafers 1 m thickness using electrochemical plating method and Cu bulk plates 99% purity, size 2 2 cm were used for the evaluation of Cu dissolution/ oxidation and Cu etch/removal rates, respectively. Cu samples were precleaned in acetone and dilute HF DHF, 0.5% solutions to remove organic contaminants and native oxides on the surface. Cu samples were treated in deionized DI water containing H2O2 at different concentrations. The concentration of dissolved Cu ions in solution was evaluated by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometer ICP-MS . After Cu was treated in H2O2 added solutions, the wettability of Cu surface and the thickness of Cu oxide were measured by a contact angle analyzer Krüss G10 static contact angle analyzer and a spectroscopic ellipsometer SE, VASE, Woollam Co , respectively. The surface morphology of Cu oxide was observed by fifield-emission scanning electron microscopy ( FESEM) .
Polishing tests were performed using a frictional polisher GNP Tech., POLI-500, Korea using an IC 1400 k-groove pad Rohm & Haas Co. . Conditioning was performed ex situ with a diamond disk. The initial break-time was 20 min at a down pressure of 0.4 psi and a rotational speed of 50 rpm. The polishing process pressure was set at 4.2 psi and the head and platen velocity were 50 and 83 rpm, respectively.
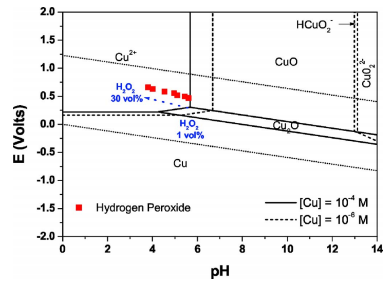
Fig1
Contact angles provide rich information on the change of surface properties such as wettability and surface morphology which are not easy to detect by other analysis methods. Figure 3 shows the change of the contact angle of the Cu surface at different treatment times as a function of the H2O2 concentration. The contact angle of precleaned Cu surface was around 40°. When Cu was treated in a solution containing H2O2, the contact angle of Cu decreased below 15° in 10 min regardless of H2O2 concentrations. The higher H2O2 concentration, the lower the contact angle was measured.
上一篇: 改善去除负光刻胶效果的方法
下一篇: 混合铝蚀刻剂的化学特性