Preparation and cleaning of the substrate is the first and most important step before thin film deposition. Substrate preparation starts from cutting and polishing of single crystal to very complex structures achieved by lithography techniques with purposes such as the removal of contaminants and native oxide layers. Many different processes are used to prepare and clean the substrate. In most cases, combinations of different techniques are used.
The contact angle measurement was measured using CAM 200 optical contact angle meter (KSV Instruments Ltd., Helsinki, Finland). A droplet of approximately 5-7 L was deposited on the surface using a syringe. The contact angles were computed based on the images of droplet on the MgO surface. For each sample a minimum of four different readings were recorded. A typical error in readings was ∼2°.
Figure 1 shows photographs of the side view of the water droplet deposited on the surface of MgO(001) substrate for the five different wet-cleaning treatments used in the present paper. The asreceived sample (labelled REF) had a hydrophobic surface with a contact angle of 80. The cleaning with the organic solvent only (fig1-b, c and d) did not improve the wettability of the surface, yielding an even higher contact angle of 96 for the AI sample. The use of a detergent clearly decreased the contact angle to a minimum of 15 for the D sample and 32 for the DAE sample. The surface of MgO cleaned using a detergent was found to be hydrophilic. This change of wettability of the surface showed that contaminants (particles, oil, wax, hydroxides, carbonates …) present on the as-received substrate (REF) was removed after a wet-cleaning process using a detergent. Wettability of the substrate is an important aspect for the chemical solution coating using spin /dip-coating or spraying of a film with homogeneous thickness. A hydrophilic surface is preferred for a good spread of the resin on the substrate, therefore a detergent step may be necessary to improve the deposition by solution on MgO(001).
The surface of the AI sample had less contaminants than the REF sample (figure 2-b). Cleaning by acetone following by isopropanol removed the contaminants responsible for the peak for Mg2s at high binding energy but the relative ratio of oxide/contaminants remains approximately the same as before the cleaning (figure 2-g). The same observation was made on the O1s peak with the absence of the component at 529.2 eV and another component at 533.0 eV which may issue from the left over of the solvent and corresponding to C-O-H or C-O-C.
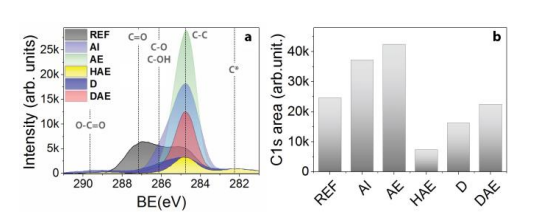
Fig1
This paper studied the effect of different wet-cleaning processes on MgO(001) substrate monitored at different stage in thin film deposition. The surface chemistry of the substrate was checked after the different wet-cleaning processes, after in-situ annealing at 700C for 2 h and after ScN thin film deposition with the study of the interface.
下一篇: SiGe的选择性化学湿刻蚀