Penyelidikan ini melaporkan fabrikasi struktur zink oksida berliang melalui proses punaran basah. Filem nipis Zn0dienapkan ke atas substrat silikon (111). Larutan pemumar yang dieunakan dalam kajian ini adalah larutan asid nitrikHNO ,) yang berkepekatan 0.1% dan .0%. Filem nipis ZnO dipunarkan selama beberapa jangka waktu yang ditetapkandan ciri-ciri struktur dan optik dikaji dengan menggunakan pembelanan sinar-X(XRD),mikroskop elektron imbasan (SEMdan spektroskopi fotoluminesen (PL). Keputusan XRD menumjukkan bahawa keamatan baei puncak ZnO(002) menuruselepas flem nipis ZnO dipunarkan dalam larutan yang berkepekatan berlainan imtuk janeka waktu yane berlainanPemerhatian ini adalah disebabkan penguraian ZnO(002) semasa proses punaran flem nipis. Imej-tmej daripadcSEM pula menumjukkan ketebalan flem nipis ZnO berkirangan denean peninekatan masa punaran.Pemerhatian iniadalah disebabkan proses pumaran isotropik oleh larutan HNO . Manakala spektrum PL pada peringkat awal punaranmenumjukkan peninekatan keamatan puncak apabila masa punaran meninekat. Namun begitu, proses punaran yangberterusan menunjukkan keamatan puncak PL mula menunjukkan trend menurun dan fenomena ini adalah disebabkapenurunan nisbah luas permukaan terhadap isi padu dalam flem nipis ZnO.
Wide-bandgap zinc oxide is a popular material becauseof its high exciton binding energy, which facilitates alasing action based on exciton recombination above roomtemperature (Ozgur et al. 2005).Although research on ZnOstarted decades ago, the use of ZnO has gained a substantialamount of renewed interest in recent years. This intereststems from the availability of high-quality ZnO substratesowing to the technological advancements and reports onthe successful deposition of the p-type conduction in ZnOfilms. This process allows the wider application of ZnO inthe research and development of devices (Chang et al. 2011).
In the present study, a set of ZnO thin films weredeposited on the p-type silicon substrates with (l1l)preferred orientation [Si(11l)] via the radio frequency (RF)magnetron sputtering method. Characterizations of thesurface morphology and the average thickness of the ZnOthin films were estimated by scanning electron microscopy(SEM).Nondestructive characterization methods, such asX-ray diffraction (XRD) and PL spectroscopy were utilizedto investigate the characteristics of the samples in depth.
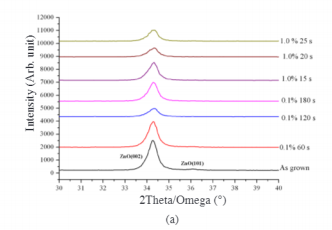
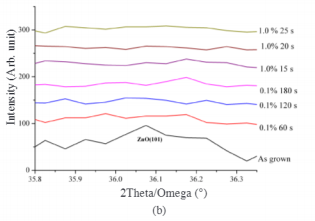
Fig1
Generally, the HNO, molecules separate to form H* andNO jons when dissolved in water. As the acid reacts with theZnO surface, Zn2+ and NO react to form a Zn(NO,), ionicbonding molecule, whereas the remaining O ions will reactwith the H+ from HNO, to form water. During this process.Zn2+ and O leave the ZnO surface, thus forming voids.
The authors are grateful for the support given by theUniversiti Sains Malaysia through the Short Term ResearchGrant (Account no: 304/PFIZIK/6311014).In addition.the support from the School of Physics, Universiti SainsMalaysia is gratefully acknowledged.
上一篇: 薄膜氧化物半导体评估系统