Abstract-- The concept of miniaturization wasintroduced because of advancement in science andtechnology during 1980s. These miniaturizedstructures and designs are of high significance formaking up with the macroscopic technology, for thesake of interfacing with microscopic world. Thefabrication of micro structures and designs which arethe advanced applications of micro fabrication areused for the process of micromachining structures inthree dimensions as it is essential for interfacing withthe nanotechnology. Micromachining which meansperforming cutting or grinding operations or selectiveremoval of wafer to produce various structures hasmuch important applications like accelerometerswhich are used to trigger air bags in cars. Thelithography and etching processes are used to shapethe bulk materials into microstructures in microfabrication mechanism. Different ion bombardmenttechniques and chemical reactive mechanisms areused for a type of etching which is carried out invacuum chamber. whereas chemical solutions areused for another type of etching mechanism whoseprocedures are finished in a bath. This surveyillustrates different etching methodologies and theimpact of various etchants in wet etching.
There are a lot of processing steps in the process ofmicro fabrication. Etching is an important step in theprocess of micro fabrication. The term etching refers tothe removal of layers from the surface of wafer whenmanufacturing. This is a critically important process. each and every wafer undergo a lot of etching process.The material which is used to protect the wafer from theetchants is known as the masking material, which is usedin many etching steps to resist etching. This maskingmaterial can be a photoresist and it is patterned usingphotolithography.Etching can also be referred as makingcavities and these cavities should have specific depthaccording to the purposes. The depth of such cavitiesproduced can be controlled by etching time and theetching rate. The success in performing etchingmechanism is that, the top layer of a multilayer structureshould be removed entirely, without any kind of damagein the underlying layers or the masking layers. Thisentirely depends on the ratio of the etch rates of twomaterials which is termed as selectivity. During somecases of etching, etches undercut the mask layer and itproduces sloping sidewalls formingcavities. Thedistance of undercutting is called bias.
Wet etching is inexpensive and it has been extensivelyused for the fabrication of MEMS components such asdiaphragms based on single crystal silicon, especially on(100) water and cantilever beam.Wet etching is theprocess ofremoving a material by using liquid chemicalsor etchants from a wafer. The specific patterns aredefined by masks on the wafer. Materials that are notprotected by the masks are etched away by liquidchemicals. These masks are deposited and patterned onthe wafers using lithography. Wet etching processinvolves multiple chemical reactions that consume theoriginal reactants and produce new reactants.
Wet etchants are often isotropic and they lead to largerbias during the etching of thick films. They also requiredisposal of large amounts of toxic waste. This etchmethod is particularly effective just before "backend"processing (BEOL), where wafers are normally very thinafter wafer backgrinding and are very sensitive tothermal or mechanical kind of stress. Etching a muchthin layer of few micrometers will remove micro cracksproduced during back grinding resulting in the waferhaving dramatically increased strength and flexibility.This type of etching is quick, easy and cheap. Roundingof sharp anisotropic corners is used to avoid stressconcentration. This exhibits same etch rate in alldirections. Lateral etch rate is about as same as thevertical etch rate. This etch rate never depends on theorientation of the mask edge.
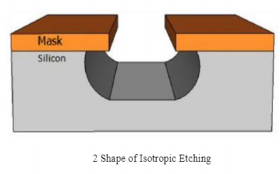
Fig1
TMAH stands for Tetra Methyl Ammonium Hydroxide.which has more advantages of all etchants used. Thisetchant exhibits low toxicity and CMOS compatibility[9]. Even though the processing time period is high foretching using TMAH than using KOHusage of TMAHgives us the best etched surfaces than the etched surfacesgot from KOH Perfect wafer squares are got at less timewhen KOH is used than that of TMAH because of etchrates for all the crystal orientations. Even though theprocessing time is less for process involving KOH theydo not provide the etched perfect wafer squares. But theadvantage of TMAH is that, even though it requires moreprocessing time periods, the etched wafer squares will beperfect. The important properties of anisotropic siliconetchants are anisotropy [8], selectivity, handling andcompatibility. The processcompatibilityprocessbecomes especially important, since sensors andactuators need to be utilized within circuits on the samechip to realize a new transducer system with highperformance.Tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide(TMAH.(CH3)4NOH)[10] solutions with variousconcentrations from 5 to 40 wt % and temperatures canbe used for wet anisotropic etching purpose. The mainfeature of TMAH is its compatibility, since it has beenutilized in the etching process as the developing solutionof positive photoresist. Thusthe semiconductor-gradesolutions can be obtained.
The etchants used for etching process are clearlydiscussed about along with the advantages anddisadvantages of the etchants in correspondence to theirrespective etchant concentration and temperature atwhich the etching process is carried out. The wafersquares which undergo etching because of the etchantsused must get the perfect wafer squares after thecompensation structures get etched off. That conditiongives us the clear idea of the processing time at whichthe perfect etch square is obtained.Some of the etchantswhich aresubjected surfactants and non-ionic to KOHand TMAH solutions. were used to evaluate the etchingproperties under various operating parameters includingthe etching rate and roughness quality of the (100)silicon plane, the selectivity of silicon dissolution towardsilicon dioxide and reduction of the undercutting atconvex corners.The etch rates of (100) and (110)decrease with increasing concentration. As theconcentration increases, the roughness of the etchedsurface is reduced and a very smooth surface isobtained.The etch rates of aluminium were reduced bydissolving silicon in TMAH solution. It was confirmedthat the etch-stop techniques using a heavily boron-doped layer or p-n junction were applicable to TMAHsolutions. It can be concluded that TMAH is a promisingsolution for silicon micromachining as one of the useful.
上一篇: 强化化学清洗工艺的处理槽腐蚀研究
下一篇: 晶圆级微透镜阵列的设计与制造