We report on GaN self-supported photonic structures consisting in freestanding waveguides coupled to photonic crystal waveguides and cavities operating in the near-infrared. GaN layers were grown on Si (111) by metal organic vapor phase epitaxy. E-beam lithography and dry etching techniques were employed to pattern the GaN layer and undercut the substrate. The combination of low-absorption in the infrared range and improved etching profifiles results in cavities with quality factors as high as 5400. The compatibility with standard Si technology should enable the development of low cost photonic devices for optical communications combining wide-bandgap III-nitride semiconductors and silicon.
However, besides the usual fabrication accuracy required for nanostructures such as PhCs, III-nitride-based materials suffer from several processing diffificulties inherited from their intrinsic properties. For instance, etching vertical and smooth sidewalls is quite challenging owing to the hardness of GaN.
In addition, membranes are highly desirable in order to guarantee a refractive index contrast as high as possible between GaN and its cladding-like due to its low refractive index (~2.3 at 1.5 lm). It is not required for SOI-based waveguides since the lower refractive index of SiO2 compared to Si provides enough contrast to confifine the light within the slab. The fabrication of freestanding III-nitride photonic structures by means of sacrifificial layers has been reported by several groups using doping-selective and bandgap-selective photoelectrochemical etching and with different III-nitride sacrifificial layers such as InGaN,AlN, and InAlN. The main disadvantage of those approaches is the limited airgap thickness that can be achieved (only a few hundreds of nanometers). This might be particularly critical for structures operating in the near infrared.
In this work, we report on the achievement of IIInitride-based freestanding waveguides and PhC cavities operating in the near infrared with Q factors of several thousands. These photonic structures are fabricated from GaN epilayers by underetching the Si (111) substrate.
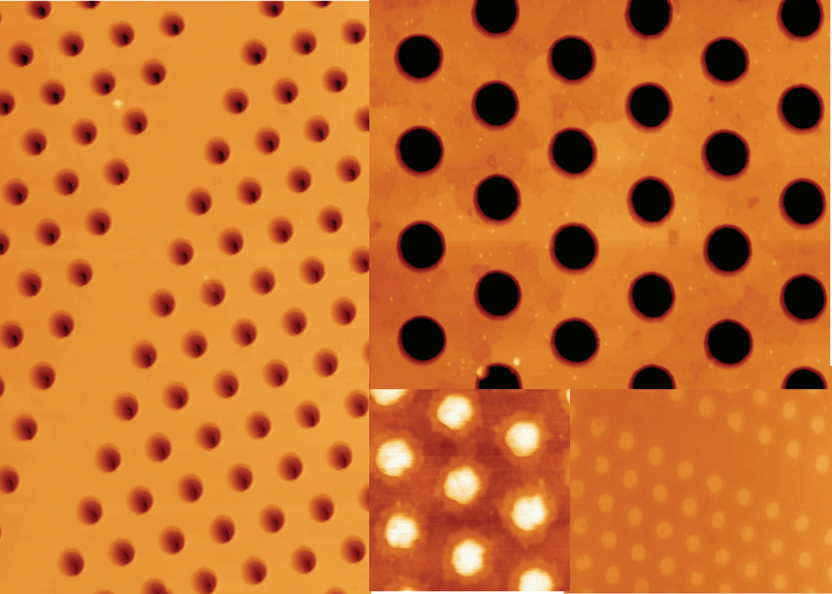
Fig2
In Fig. 2, scanning electron microscope (SEM) and optical microscope images of the actual structures are displayed. In Fig. 2(a), a L3 cavity together with the W1 waveguide is shown. One can observe the high regularity of the PhC lattice. The smooth and vertical profifiles of the holes sidewalls are shown in the inset of Fig. 2(a). Note that our process allowed us achieving a high verticality of the sidewalls (< 5% ) with an aspect ratio of 3.24 The pink-green contrast in the optical image (Fig. 2(b)) delimits the undercut areas (pink-like) and the 3 lm thick airgap is clearly evidenced in Fig. 2(c). Such large airgap confifirms the high selectivity between III-nitrides and Si (111), which makes this fabrication process promising for the integration of III-nitrides on Si platforms.
The authors would like to thank R. Butt!e for fruitful discussions and a critical reading of the manuscript, Z. Benes for technical e-beam lithography advices, and N. Kaufmann for AFM measurements. This work was supported by the NCCR Quantum Photonics, research instrument of the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) and by the SNSF.