The typical growth of MoS2 involves carrier gases of 350 sccm Ar, 10 sccm of H2 and 8 sccm of diethyl sulphide at the growth temperature of 850◦ C for ~20 min. The hydrogen flow plays double roles during the synthesis process: Vaporization of precursors and desulfurization of MoS2 flakes, which lead to growing and etching of MoS2 flakes, individually.1,2 Thus, it is important to apply the appropriate amount of H2 during the synthesis of the MoS2. To optimize the H2 flow, different flows of H2 were applied during the growth procedures. Figure S1 shows the effect of various H2 flow rates on the quality of the MoS2 film on SiO2 at the sodium molybdate (Na2MoO4) concentration of 0.006 M. Clearly, the nucleation density of MoS2 can be substantially decreased at the optimal H2 flow rate of 10 sccm.
The fingerprint Raman peaks of MoS2 at 384 cm−1 and 403 cm−1 correspond to the in- plane vibrational mode E’2g and out-of-plane mode A1g respectively for as-grown MoS2 on sapphire. The relative distance of the two peaks is strongly refected by the thickness of MoS2 film.3 Figure S3 shows the widths for monolayer, bilayer, and multilayer (at the nucleation sites) of MoS2 are 19 cm−1 , 21.3 cm−1 and 25.7 cm−1 , individually.
To check the atomic structure of grown MoS2, as-grown MoS2 films need to be transferred onto transmission electron microscopy (TEM) grids. Figure S5 shows a representative trans- ferred MoS2 film on a SiN TEM grid with multi-magnification of optical images.
After transferring as-grown MoS2 onto SiO2 or TEM grids, the remained sapphire substrates were cleaned in an ultrasonic bath with acetone, isopropanol and deionized (DI) water. Subsequently, the cleaned sapphire substrates were annealed in the quartz tube in air at 1100◦ C for 1 h.
Afterward, these sapphire substrates were treated with KOH, spin-coated with sodium molybdate, and then placed in the quartz tube for the second time of growth. After finishing growth, the MoS2 film was transferred, and the sapphire substrate is again used for the third time of growth after the cleaning cycle. The repeated growth samples were checked with an optical microscope, as displayed in the Figure S6.
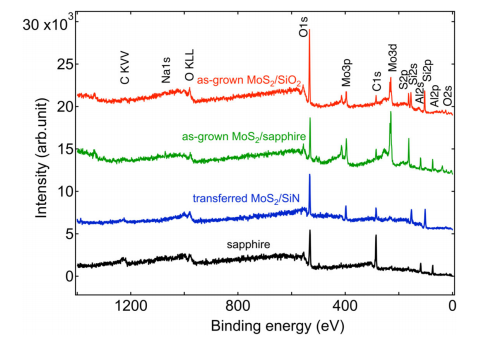
Fig s4
The XPS survey spectra of as-grown monolayer MoS2 on sapphire, on SiO2, and after transfer onto SiO2 and SiN substrates in Figure 3 of the main text were measured before and after the wet-transfer, as displayed in Figure S4.