Porous silicon (PS) was prepared by electrochemical etching method. Mirage effect in transverse photothermal deflection PTD ( skimming configuration) was used to determine thermal conductivity the experimental results of PS thermal conductivity was compared with theoretical results they were almost the same. Optical extinction coefficient and absorption coefficient were calculated from transmittance T and reflectance R curve which measured with UV-Vis-NIR Spectrophotometer, and they were used to calculate the optical conductivity and electric conductivity from the Shankar and Joseph equations, and optical conductivity and electric conductivity were studied with porosity in porous silicon.
Porous silicon has attracted considerable research interest after their discovery in 1956. Low-dimensional materials are finding ever-widening application in many areas of science and Engineering. Nanostructured porous silicon shows a variety of other interesting properties, including tunable refractive index, tunable energy gap, low light absorption in the visible, high internal surface, variable surface chemistry, or high chemical reactivity. Properties, along with its ease of fabrication and the possibility of producing precisely controlled layered structures make this material adequate for its use in a wide range of fields, such as optics, micro- and optoelectronics, chemical sensing or biomedical applications .
Porous silicon samples were prepared by electrochemical etching method of p-type cubic silicon wafers (c-Si), (100) orientation with resistivity of 0.01-40 Ω·cm, electrochemical dissolution of Si wafers is used: HF-ethanol (measured by volume) aquas with concentration from 20% . The current density was always kept Constant for each sample during etching of PS (10,..,50 mA/cm2).Fabricating process done in a normal etching Teflon cell fig(1). After anodization, PS samples are carefully removed from the bath and cleaned in deionized water . Few examples of AFM measurement is presented to show differences between samples according to preparing current (fig.2).
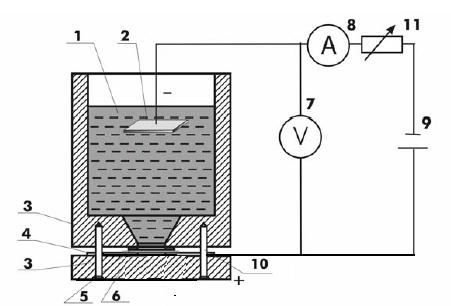
Fig1
Porosity is defined as the fraction of void within the porous silicon PS layer and can be determined easily by weight measurements. The virgin wafer is first weighed before anodisation (m1), then just after anodisation (m2) and finally after dissolution of the whole porous layer in a molar KOH aqueous solution (m3). the removal is made through a dip for some minutes in an aqueous solution of KOH (3% in volume), that leads to a selective removal of the PS layer without reacting with the bulk crystalline silicon.
Different techniques are employed to determine the porous layer thickness d. From the gravimetric measurements, where is the silicon density and S the etched surface.
The decreasing in Thermal conductivity is attributed to that: The solid contribution is normally significantly higher than that of the gas contained in the pores, and thus, the gaseous conduction contribution is considered to be negligible. The radiative contribution, krad, is derived from heat radiated throughout the pores, and is highly dependent on the porosity, pore size, and temperature. For all that reasons thermal conductivity in bulk silicon is higher than that of PS samples. fig(4) shows the measured and theoretical calculated thermal conductivity of PS sample they are almost the same.
Porous silicon samples were prepared by electrochemical etching method , HF-ethanol concentration from 20% ,The current density was (10,..,50 mA/cm2 ).Fabricating process done in a normal etching Teflon cell, Mirage effect in transverse photothermal deflection PTD ( skimming configuration) is used to determine effective thermal conductivity . It changed from 120W/Mk for 8% porosity to 47.2 W/Mk for 69 % porosity. Experimental results of PS thermal conductivity with porosity was compared with theoretical results and it was almost the same . Absorption coefficient was calculated from transmittance T and reflectance R curve measured with UV-Vis-NIR Spectrophotometer was used to calculated extinction coefficient then to calculate electric conductivity and optical conductivity, our work shows that absorption coefficient and the extinction coefficient decreases with porosity increases. So is electric conductivity, while optical conductivity remains constant in rang of our porosity.
上一篇: NiW 合金电镀填充 TSV